What is Web Application Architecture?
Web Application Architecture is a framework that is comprised of the relationships and interactions between application components, such as middleware systems, user interfaces, and databases. The general concept of Web Application Architecture is in line with the concept of a browser user who triggers an application that is capable of running in multiple websites.
In essence, Web Application Architectures can be defined with the depiction of this process:
- A user browses for a specific URL, which the browser locates and requests.
- Over the network, data is sent from the server to the browser, then executed by the browser so that it is able to display the requested page.
- The user views and interacts with the page.
As explained by DZone, Web Application Architecture includes all sub-components and external application interchanges for an entire software application.
As the tech world continues to evolve, applications are considered a spearhead in this transformational process. Modern application architecture and its development are continuously improving in both of its frontend and backend capabilities.
Specifically, on the backend or server side, there are numerous application development architecture approaches that are emerging to cope with and solve current development needs such as microservices, serverless architectures, and single page applications. In an upcoming section, we will provide more details about the different types of Web Application Architectures.
Over the last few years, the preferred platform to deliver content and services has been the web. Thus, companies of all shapes and sizes needed to be online and present for their prospects and regular clients.
Nowadays, having an online presence also means being mobile as more and more web access originates with mobile devices. Mobile application architecture plays a key role in how developers approach client requirements to ensure there are consistency and availability across all platforms. As more complexity is added to applications, developers, in turn, become less specialized in covering multiple development skills. Full stack development architecture embodies a significant volume of information and tools that piece together a web application. As the lines blur between frontend and backend development, full stack development architecture works with both. It’s noteworthy to mention that REST API helps numerous platforms work with backend development.
Components of Web Applications Architectures
As previously stated, Web application architectures are comprised of several components that help build its digital makeup.
These components can be categorized into two areas: user interface app components and structural components.
User interface app components refer to web pages displaying dashboards, logs, notifications, configuration settings, and more. They are not relevant to the structural development of the application and are more user interface/experience oriented.
The structural components, which are the real meat of the app development process, are:
- The web browser or client.
- The web application server.
- The database server.
The web browser or client is the interface rendition of a web app functionality, with which the user interacts with. This content delivered to the client can be developed using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS and doesn’t require operating system related adaptations. In essence, the web browser or client manages how end users interact with the application.
The web application server manages business logic and data persistence and can be built using PHP, Python, Java, Ruby, .NET, Node.js, among other languages. It’s comprised of at least a centralized hub or control center to support multi-layer applications.
The database server provides and stores relevant data for the application. Additionally, it may also supply the business logic and other information that is managed by the web application server.
Types of Web Application Architecture
There are three, well-known Web Application Architecture types available in the modern tech landscape.
These types of Web Application Architectures are:
- Single Page Applications (SPA): Modern, efficient applications are designed to only request the most necessary elements of content and information to generate an intuitive and interactive user experience. Single page web applications interact with the user in a more dynamic fashion by providing updated content within the current page, rather than loading entirely new pages from the server with each action from the user. This helps prevent interruptions in the user experience, transforming the behavior of the application such that it resembles a traditional desktop application. The most heavyweight player is AJAX, short for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML, which is the foundation for page communications making SPAs possible.
- Microservices: Microservices are small, lightweight services that execute a specific, single functionality. The Microservices Architecture framework offers a comprehensive set of advantages that help developers be more productive and speed up the deployment process of bespoke software applications. Since the components in the application are not directly dependent on each other they do not need to be developed in the same coding language; developers have free range to work with the technology stack of their choice that works best for the needs of the service and in the desired timeframe.
- Serverless Architectures: This approach leverages third-party cloud infrastructure services to outsource server and infrastructure management allowing applications to execute required or custom logic without concerning themselves with the infrastructure related tasks While it is somewhat similar to Microservices, the development entity does not own or manage the backend servers, which makes it simpler when the development company does not want to manage or support the servers and the hardware they run in.
Web Server Architecture
The Techopedia definition of the Web Server Architecture states that it is the logical layout or design of a web server, based on which a web server is designed, developed and deployed.
The essential purpose of a web server architecture is to complete requests made by clients for a website. The clients are typically browsers and mobile apps that make requests using secure HTTPs protocol, either for page resources or a REST API.
The web server architecture structure is comprised of: a physical capacity of the server in terms of computing power, storage, and memory, performance, and app tiers which include the different types of apps within the server, operating systems, and network connectivity.
Java Web Application Architecture
The Java Web Application Architecture has traditionally been a favorite in the enterprise development environment due to its versatility. Currently, Java is the undisputed top-player among the most favored programming languages.
The complexity of a web application architecture depends solely on the requirements of the desired solution. Whether it’s a simple, informative web application or a robust, multi-tiered web application, Java Web Application Architecture technologies can help achieve successful results.
The Java Web Application Architecture can combine and work with a number of Java native tools to build a web application. You can pick and choose from a wide array of available Java products and frameworks to create everything from simple web applications to full-fledged enterprise-wide systems.
Mobile Application Architecture
Mobile Application Architecture is the framework of tools, techniques, and technologies needed to build a mobile application. This specific framework takes into careful consideration the procedures that are needed to ensure an application works properly and efficiently in a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet.
In a Mobile Application Architecture, the device, navigation, bandwidth and user interface must be thoroughly taken into account to design an adequate solution for the mobile app architecture.
Device. Device-specific components that ensure the app is supported, covering aspects such as operating systems (iOS, Android), screen size, CPU details, resolution, storage space, and more.
Navigation. This design element analyzes and employs specific details that may be required of a mobile application such as view, navigation bar, scroll views, search capabilities, and more.
Bandwidth. Mobile applications rely heavily on connectivity to perform to their full extent. Software and hardware must be considered to handle caching, intermittent connectivity, batch communications, and more.
User Interface. Ultimately, this is what the client sees, uses, and interacts with.
The design flow of the Mobile Application Architecture is comprised of these building blocks:
- Presentation layer: User interface components that address how an application is viewed by the end user. It also deals with the user interface process components.
- Business layer: This layer focuses on the behaviors available to the end users. It includes workflows and entities that deliver the functionality of the application.
- Data layer: At the heart of the mobile application, data powers a secure application structure and cognitive environment for the application. All data functionalities should be able to scale for future requirements.
Node.js Web Application Architecture
Node.js Web Application Architecture has become a strong candidate to develop web applications. More and more developers feel comfortable with the Node.js framework to solve design and structural requirements in application development architecture. Node.js is written using JavaScript and is the same technology as frontend components, which makes it easier for the same developers to program backend services and frontend user interfaces.
Node.js Web Application Architecture provides speed and efficiency to the development environment, making it a key player in the industry. At its heart, Node.js was designed with integrations in mind, which comes as no surprise since more and more enterprises are leveraging this framework to integrate numerous services and systems through a single user interface.
The Node.js Web Application architecture provides coherence, code sharing and reusability, simple knowledge-transfer, and a large number of free tools.
These benefits bring flexibility and efficiency when building a reliable web application.
Ruby on Rails Web Application Development
Identified as one of the most notable contenders in app development, the Ruby on Rails Web Application Development framework is an easy to use, open-source software that places top importance on the developers' happiness.
Additionally, the Ruby on Rails Web Application Development framework focuses heavily on productivity and rapid web development. To achieve this productive, fast-paced environment, Ruby on Rails relies on the “Convention over Configuration” concept. In essence, conventions are assumptions that are considered the best solution to complete a specific task. This simplifies the developer’s life because conventions are used to deliberate and make decisions where necessary, unloading the developer’s plate.
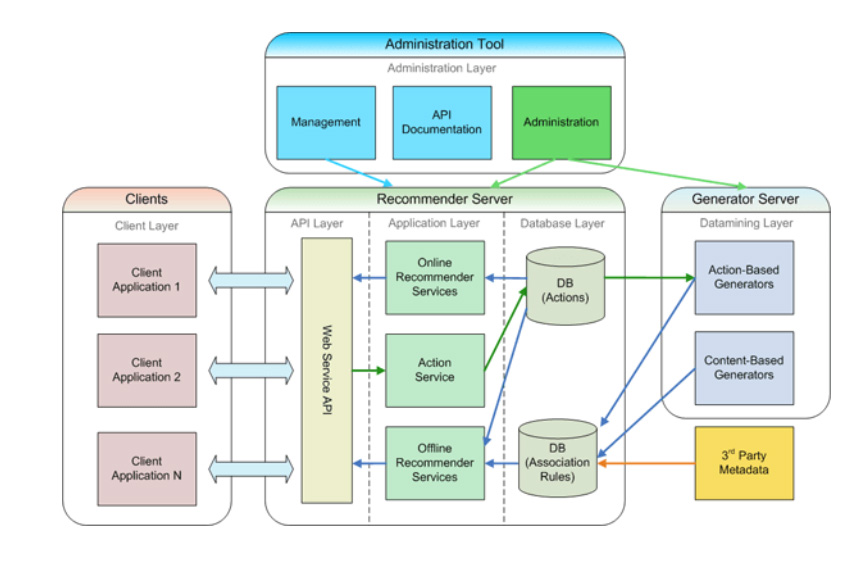
Web Application Architecture Diagram
This Wikipedia Web Application Architecture diagram depicts how the framework works:
Expertise for Web Application Architecture
Modern application architecture works better on multiple platforms and multiple devices. This is a result of a well-developed architecture that is the foundation of a successful operability.
In essence, a healthy Web Application Architecture must be easy to use, solve problems, offer a fast response time, use the latest and most secure standards, avoid failures with self-healing capabilities, allow growth, and ultimately, provide an effortless user experience.
Please contact our team o for more information. We will be happy to assist you.

