Software Development Life Cycle Methodologies
What is SDLC?
Software development is the bread and butter of software engineers and developers all around. Every day, software engineers and professionals alike have to immerse themselves into the dynamics of the best Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) methodology and approach to develop and deliver software in optimum conditions. But, what is SDLC?
In the simplest terms, SDLC methodologies provide a systematic framework to design, develop and deliver software applications, from beginning to end. It is a series of steps that offer a foundation for the software development process. Having a structure to develop software is fundamental, which is why there are multiple software development methodologies available to choose from. It is increasingly important for software engineers to select the right SDLC model that meets specific requirements and concerns of the project to drive success. In this article, we go into the details of SDLC methodologies, their relevance, their advantages, disadvantages, and everything in between.
To a certain extent, SDLC methodologies can be thought of like a checklist of the different stages that must be performed to develop and deliver successful software applications. All SDLC methodologies share a common ground of distinct phases that include planning, analysis, design, building, testing, deploying, and maintenance. These SDLC phases provide the outline of what a software application project entails.
In the following section, we are going to explore how software development lifecycles impact the software development process.
The Software Development Process
The software development process, as with all great projects, starts with an idea. It takes planning, preparation, and management of phases and team members to reach a goal. SDLC is a mapped-out, regulated framework that typically follows the following universal phases to deliver high-quality software application.
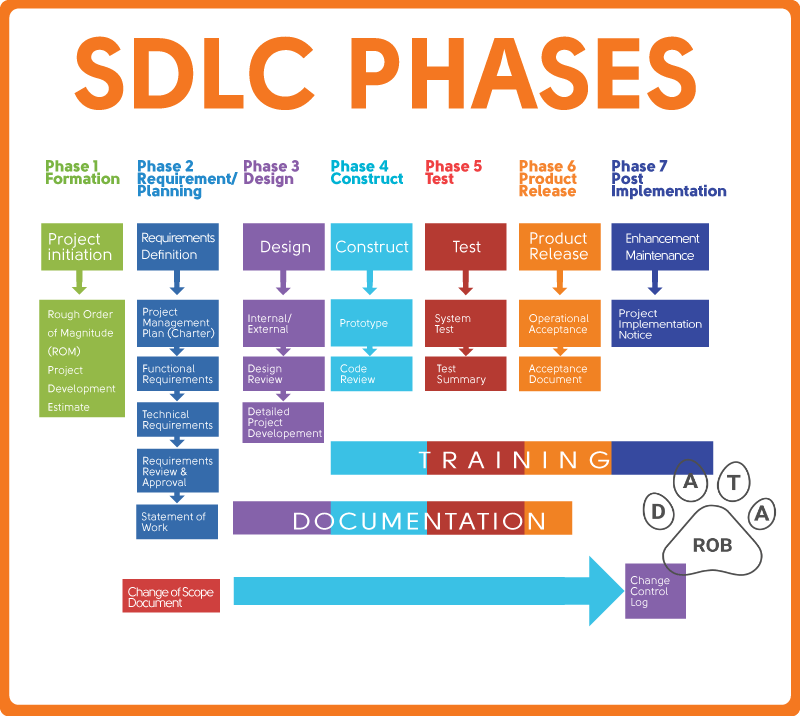
SDLC phases
Formation phase
This basic, initial phase is the inception of an idea for a solution that improves an existing solution or develops an entirely new one. It helps define the magnitude of the project to plan resources.
Requirement/Planning Phase
In this phase, requirements are gathered to formulate a design plan for the software application solution. This phase entails a thorough analysis to assess user needs, feasibility, development, improvements, and more. It is very important to include documentation to refine requirements and keep a record of the solution’s development. This phase involves the creation of a project charter which defines technical and functional requirements.
Design Phase
This phase is focused on the design aspect of the software application solution in terms of the selected technical and functional requirements and the results of the thorough analysis of the software’s viability.
Development Phase
This phase is the “meat” of the software development process. In this phase, software engineers are solely focused on building a prototype of the solution to perform a code review and ultimately create the solution itself. The team works on transforming software specifications into a working and reliable solution.
Testing Phase
This crucial phase tests the software to ensure that everything works as it intended. In the testing phase, software engineers are able to detect defects, bugs, and errors in the software solution and ultimately have a quality product that meets business expectations. Quality Assurance (QA) specialists perform a series of tests to evaluate the status of the solution.
Release Phase
Once the software application is fully developed and tested, it moves to the release phase. In this phase, the software goes live and is released to the end user for actual use of the product. In essence, the software is fully operational in a live environment where end users utilize it.
Maintenance Phase
This post-release phase is tasked with keeping the software completely operational, updating it to meet quality standards, and enhancing it throughout its life to ensure it continues to attract and retain users.
The software development process sets the tone and defines a goal from which developers kick-start a project. Ultimately, following a software development process is intended to develop software faster and with a few hiccups as possible.
Now that we’ve covered the universal SDLC phases, let’s assess how important it is to follow software development methodologies in an IT environment.
The importance of SDLC methodologies in an IT project
It is rather unrealistic to think of a software development environment where structure and defined processes aren’t needed. In an atmosphere where there are so many variables, players and things that can go wrong, it is imperative to have the help of guidelines and a “rulebook” you can use as a standard to guide you through the process of delivering a successful software application.
The importance of having and following prescribed methodologies in software development lies in the predictability of having a controlled environment for all development efforts. Software Development cycles or methodologies, in essence, are a series of stages or steps through which an organism, or in this case, a software application, passes through in a series of recurrences to reach the desired outcome. The lifecycle in software development follows the life of a software application from its inception to its maintenance, and developers need a level of control to ensure the solution is consistent with the original requirements and the release of the solution is properly managed.
Methodologies in software development are repeatable processes that can be reused as many times as necessary with a strong likelihood of delivering successful results if applied correctly.
Working under SDLC methodologies provides the opportunity to deploy solutions faster because it is a consistent, repeatable and systematic approach. Additionally, it allows organizations to respond better to market pressure and deliver high-quality business applications due to its structure and systematic nature which enables developers to work in a controlled environment.
Next, we are going to cover some of the different software development methodologies available to help users select the right fit for their solution.
Selecting the right SDLC methodology for a project
In this section, we are going to cover some of the most prominent types of SDLC methodologies, which are:
Waterfall
Known as the traditional methodology, Waterfall is a sequential and linear flow for developing a software application. The process is outlined by a series of finite stages, each of which must be fully completed before moving on to the next one. The Waterfall approach follows this order: requirements, design, execution, testing, and release.
Advantages of Waterfall
It is structured and easy to follow. The activities are well defined and it fosters careful planning of the project. Additionally, it has specific deliverables at each stage of the process.
Drawbacks of Waterfall
It is unyielding and complex to go back to any stage after it is finished. It has little flexibility to adjust to a changing scope. Additionally, it is relatively more expensive than other methodologies and is more time-consuming.
Prototyping
This methodology creates prototypes of the software application to simulate the functioning aspects of a desired, final product. Prototyping is mainly used to visualize components of the software solution and match them with customer requirements. There are several variants of prototyping but they are mainly categorized into throwaway and evolutionary. Throwaway prototyping creates a model that will eventually be discarded and evolutionary prototyping refers to a robust prototype that will be constantly refined to reach its final version.
Advantages of Prototyping
A functioning version of the software solution can help identify potential risks and threats that can be dealt with in a timely manner, reducing costs and time investment. Additionally, the user is involved and can visualize a working version of the software.
Drawbacks of Prototyping
A working prototype may cause confusion with the finished version of the system. Oftentimes, developers end up wasting a significant amount of time creating a prototype, and their time could have been t used in a more valuable manner. Additionally, it can be costly to implement functioning prototypes.
Spiral
The Spiral methodology can be thought of as a combination of the Waterfall methodology and the prototyping methodology. It is typically the methodology of choice for large and complex projects because it uses the same stages as the Waterfall methodology but it separates them into planning, risk assessment, and prototype building.
Advantages of Spiral
It provides more realistic estimates in terms of workloads, budget, and schedule as it discovers challenges and issues in its early stages. It involves developers right from the get-go and manages both risks and the system’s development in small phases of segments.
Drawbacks of Spiral
It is a costly methodology that consumes a significant amount of time to reach the desired solution. Additionally, it requires a team of highly-skilled specialists who help evaluate risks and assumptions.
Agile
The iterative and incremental methodology known for excellence, Agile is a framework that evolves through collaboration between teams. It is a dynamic and interactive methodology that works in sprints that have a defined duration with lightweight deliverables that help reduce the time in which software is released. It advocates for adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, continuous improvement, and rapid and flexible responsiveness to changes.
Advantages of Agile
High-quality software, which can then be further built upon with successive iterations, is delivered in the least possible amount of time. It includes a deep involvement from the client but it remains a very flexible methodology as changes can be introduced at virtually any stage of the project. Additionally, Agile fosters a high degree of collaboration between cross-functional teams and all the involved parties.
Drawbacks of Agile
It requires a team of specialized developers who are solely focused on the project at hand and have a specific set of skills. Agile can be challenging when scaling projects and it also presents constant refactoring as changes are frequent and even more so if the scope is not properly defined from the early stages of the project.
Iterative and incremental
The iterative and incremental methodology is designed to overcome any fault or shortcoming of the Waterfall methodology. The iterative and incremental methodology begins with initial planning and ends with the deployment of the solution, with cyclic interaction in between. In essence, it develops a software application via iterative and repeated cycles that are performed incrementally so developers can learn from the development of previous portions of the software.
Advantages of iterative and incremental
It delivers business value early in the development lifecycle and makes better use of limited resources via incremental development. It is flexible enough to adapt to changing requests between increments and is more customer-focused than linear approaches.
Drawbacks of iterative and incremental
This methodology requires heavy documentation efforts as it follows a stringent set of processes. It requires a deep level of customer involvement and can turn problematic when delimiting functions and features.
V model
V model methodology is considered an extension of the Waterfall methodology, but instead of flowing down in a linear way, the steps are designed upward to form a V shape. In this methodology, the relationships between each phase of the development lifecycle are associated with a testing phase. The horizontal and vertical axes display the time or project completeness (left to right) and abstraction level (coarsest-grain abstraction).
Advantages of V model
It is relatively easy to use and understand as it has specific deliverables throughout each phase of the process. It carries out test plans early on in the lifecycle which helps verify and validate the product from the beginning.
Drawbacks of V model
It is considered an inflexible model which makes it difficult to adjust the project’s scope, which can ultimately turn expensive. There are no early prototypes of the software and no clear path for issues discovered during the testing phases.
This summary of some of the most prominent SDLC methodologies paints an illustrative description of what each solution entails and which one is best suited for specific project needs and requirements, thus making it easier to select the right methodology.
Next, we are going to talk about some of the most popular SDLC models.
Popular SDLC models
These are some of the most popular SDLC models.
Continuous integration
With Continuous Integration (CI), users can detect problems from the build of a software application to its basic deployment. CI allows users to detect and fix problems before they have the chance to cause significant damage. In many environments, CI is considered a necessity for Agile frameworks and to help meet business demands. In essence, with Continuous Integration, all developer work copies are merged into shared mainline multiple times a day to prevent integration problems.
Prototyping
In this model, a prototype is built and developed to act, feel, and behave like an early approximation of a final software solution. An ideal prototype displays the expected functionality of a product under development and is frequently used to demonstrate to customers who may not have specific project requirements how the software can look and function. Usually, a prototype is reworked and refined until it reaches an acceptability stage from which a finalized solution can be developed.
Incremental development
The incremental development model involves the design, implementation and incremental testing of a software product until the product is finished. The software product is not considered finished until it meets all of the functional and technical requirements that were initially delimited. It combines elements from the waterfall and prototyping methodologies.
Rapid application development (RAD)
It is an adaptive approach that puts less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on an adaptive process. Oftentimes, prototypes are used in RAD to substitute design specifications. RAD is considered one of the most popular SDLC models for software that is driven by user interface requirements. From its origin, RAD was created as a response to the plan-driven Waterfall methodology that designs and builds things almost as structured as done with a building. RAD is all about fast prototyping and iterative delivery that falls into the parental category of Agile.
These models help implement and take the most advantage of software development processes.
Conclusion
SDLC methodologies are here to stay and evolve. These systematic solutions to the challenge of developing software are a great starting point for developers who embark upon the valuable task of creating a software application solution.
Whether you are an advocate of a specific methodology or solution, it is important to recognize the inherent value and importance of selecting the right methodology for your software project. We have an outstanding team of dedicated professionals who are skilled, highly-specialized, and experts in helping design, build and deploy software solutions that are successful for your needs.
For more information, reach out to us and we’ll be happy to provide more details and all the help you’ll need to reach your software development goals.